Fertility rate is explained as the total number of children that would be born to a woman during her child-bearing years.
Total Fertility Rate (TFR) = (The sum of the Age Specific Fertility Rates x The number of years in each age group) / 1000
Total fertility rate (TFR) is a very important factor in a country’s population growth.
Another factor that influences a country’s total population is life expectancy.
Must Read: How can the total fertility rate change
Therefore, TFR and life expectancy are interdependent and influence a country’s population.
(Data source: United Nations)
Required ideal fertility rate
To maintain an adequate population, women, on average, are required to have 2.1 children.
Therefore the total fertility required is 2.1.
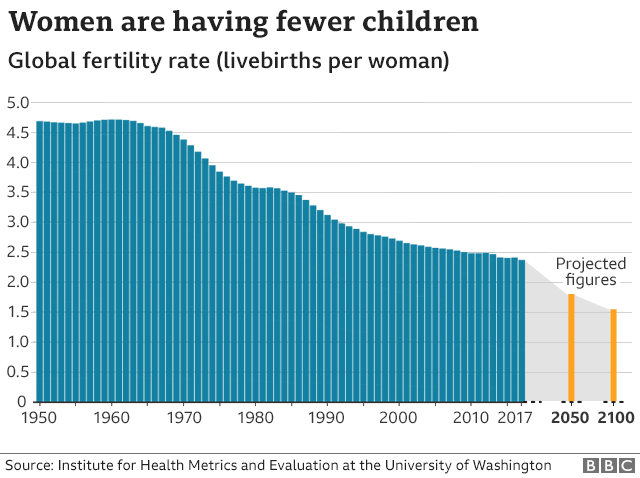
As of 2018, the world’s fertility rate was 2.4 children per woman.
The current fertility rate for the world in 2021 is 2.438 per woman.
This is 0.41% of decline from 2020.
(Data Source: United Nations – World Population Prospects)
A view and discussion
When you notice the above TFR and the dropping fertility rate, it’s a bit disappointing. Right?
Globally this is happening right now as men and women are preferring to have less number of children.
Although there may be many reasons attached to it, it is important to note that, for the future generations, this may not be a good sign.
Therefore, it becomes a great responsibility for the current older population to encourage and motivate their families to focus on offspring.
That is to have more children.
If a viewpoint is made on global fertility rate, to name few countries,
Russia, Italy, Europe and many other countries are emphasising on having more children. In fact families with two or more children are receiving financial benefits per month.
Generous family and social benefits play a huge role in the successful building of a family. Swedish parents are already receiving 480 days of paid parental leave and men are able to claim 30% of all leave.
India
The current government in Assam recently stated that those who have more than two children will not be able to get government jobs or avail benefits like government housing or content in local body elections.
Korea
South Korea having the lowest birth rate is now encouraging people to have more kids.
Additionally they are also offering childcare facilities and other incentives for parents.
So, employees are returning home early and leaving their offices.
They also passed a rule in 2010 to turn off the lights in its offices at 7.30 pm on the third wednesday of every month, so that people can go home early.
Singapore
Singapore is spending over $1.3 billion on its policies to encourage parents to have more children.
It is also providing tax cuts and extended maternity leave.
Japan
Japan’s fertility rate is at its highest in over two decades and it was 1.46 in 2015. The economic growth of the nation has helped people to receive perks and incentives for new born births. In addition to this, Tokyo awards a one-time payment of $1700 per birth and another gives $940 for the first kid and 10 times as much for the fourth baby.
France
France has the highest fertility rate in Europe with 2.01. In 2016, France spent 2.6% of its GDP on helping families.
France offers 16 weeks of maternity leave for the first kid. Increases to 26 weeks for the third child.
The government also offers excellent childcare support and other incentives.
Africa
African countries have the highest birth rates in the world.
India & South Africa
India and South Africa have the highest birth rate among BRICS (BRICS joins five major emerging economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa) countries with 2.4 annual births per 1,000 people.
According to the U.N. the world’s population is expected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050.
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
UNICEF Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) have been adopted by all United Nations Member States in 2015.
The SDG goals are :
- No Poverty
- Zero hunger
- Good health and well-being
- Quality education
- Gender equality
- Clean water and sanitation
- Affordable and clean energy
- Decent work and economic growth
- Industry, innovation and infrastructure
- Reduced inequalities
- Sustainable cities and communities
- Climate action
- Life below water
- Life on land
- Peace, justice and strong institutions
- Partnership for the goals
- Responsible consumption and production
UNICEF states that SDGs cannot be achieved without achieving child rights. According to 2030 promise, children globally must secure good health, quality education and a clean planet.
Children are the leaders of tomorrow and their abilities must be built to protect the future and therefore they deserve to secure their rights today.
UNICEF works with governments, UN agencies, partners and other alliances to help countries to achieve the goals for every child and to achieve this 100 Member states have renewed their commitment.
Understanding fertility rate in men and women
A deep shrink in the total fertility rate requires necessary care and that is to care for couples to take care of their health and stay high in fertility rate to have children naturally.
Fertility rate dropping
Although the economic and financial factors play a bigger role in fertility dropping, this aspect requires good attention in helping young men and women to stay healthy and take care of their health by adding quality diet and nutrition to stay physically fit.
The researchers are cautioning women to give less emphasis on education and access to contraception.
Prof Stein Emil Vollset said: “Responding to population decline is likely to become an overriding policy concern in many nations, but must not compromise efforts to enhance women’s reproductive health or progress on women’s rights.” (Source: BBC health)
2.1 Fertility Rate maintain to stop fertility rate decreasing
On a global level, there are some countries where the fertility rate is decreasing and this is not a good sign.
2.1 is the fertility rate that must be maintained globally.
That is to have two children so the population stays active.
Nations that are having higher childhood mortality need a higher fertility rate.
The impact of pandemic on current global fertility rate 2021
Economic recession and poverty have brought a lot of variation in fertility rates. Particularly in the pandemic period, it is one of the biggest causes of fertility rate dropping. It is also stated that it may have a long-term impact on fertility rate even after recovering from the pandemic period.